Setting up Forgejo-runner in a Fedora server with rootless podman
Here we assume you are using a freshly setup Fedora 42 server without any extra packages installed. We also assume you have a working Forgejo server (or you are using an already existing one).
First we download the required binaries following the official tutorial - we however modify the gpg key import line by adding hkps:// at the start.
$ export RUNNER_VERSION=$(curl -X 'GET' https://data.forgejo.org/api/v1/repos/forgejo/runner/releases/latest | jq .name -r | cut -c 2-)
$ wget -O forgejo-runner https://code.forgejo.org/forgejo/runner/releases/download/v${RUNNER_VERSION}/forgejo-runner-${RUNNER_VERSION}-linux-amd64
$ chmod +x forgejo-runner
$ wget -O forgejo-runner.asc https://code.forgejo.org/forgejo/runner/releases/download/v${RUNNER_VERSION}/forgejo-runner-${RUNNER_VERSION}-linux-amd64.asc
$ gpg --keyserver hkps://keys.openpgp.org --recv EB114F5E6C0DC2BCDD183550A4B61A2DC5923710
$ gpg --verify forgejo-runner.asc forgejo-runner
Good signature from "Forgejo <contact@forgejo.org>"
aka "Forgejo Releases <release@forgejo.org>"We copy the runner as usual to where bin files are located, so that we can call it directly in bash.
$ cp forgejo-runner /usr/local/bin/forgejo-runner
$ forgejo-runner -v
forgejo-runner version v11.2.0You may now install podman.
$ dnf install podman -yNow, remember, we intend to use rootless podman as the container backend for forgejo-runner. We therefor need a user (not root) to run these pods. For complete instructions indicating gotchas and things to verify on your system, refer to podman's official rootless tutorial (notable for subuids and subgids).
$ useradd --create-home runner # Create user.
$ loginctl enable-linger runnerAt this point, you should create an ssh key pair for the user runner and access it through ssh. Running su -l or su will not properly initialize environment variables nor will it initialize the systemd user session properly (necessary for cgroupv2), so this must be avoided. Enabling linger is mandatory as the runner user is not guaranteed to be logged in at all times, yet we need its session. You can use systemd-run alternatively. Here is an improper setup of ssh keys just for the convenience of this tutorial.
$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f /root/.ssh/runner_key -P ''
$ cat .ssh/runner_key.pub >> /home/runner/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ systemctl restart sshd
Now running ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost from root should throw you into an ssh session as runner. But I reiterate, this is a quick hack for this tutorial - You are better off setting up a proper key pair and connecting through ssh the proper way.
$ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost podman version
Client: Podman Engine
Version: 5.6.2
API Version: 5.6.2
Go Version: go1.24.7
Git Commit: 9dd5e1ed33830612bc200d7a13db00af6ab865a4
Built: Tue Sep 30 00:00:00 2025
Build Origin: Fedora Project
OS/Arch: linux/amd64$ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'podman run --rm --volume "$PWD:/data:ro" --workdir /data alpine sh -c "ls -lisa;pwd"'
Resolved "alpine" as an alias (/etc/containers/registries.conf.d/000-shortnames.conf)
Trying to pull docker.io/library/alpine:latest...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob sha256:[REDACTED]
Copying config sha256:[REDACTED]
Writing manifest to image destination
total 48
130323 4 drwx------ 6 root root 4096 Oct 1 20:36 .
131206 8 dr-xr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Oct 1 20:54 ..
[REDACTED]
/data
$ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'echo $XDG_RUNTIME_DIR'
/run/user/1000
$ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'forgejo-runner --version'
forgejo-runner version v11.2.0
If the above commands run without issue (note that the before-last command should not return /run/user/0 nor be empty), then the installation of podman and forgejo should have been successful. Now enable the socket for the user runner as per Forgejo documentation
$ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'systemctl --user enable --now podman'
Created symlink '/home/runner/.config/systemd/user/default.target.wants/podman.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/user/podman.service'.Now onto registering the forgejo-runner. Generate the registration token associated to your user, forgejo instance or organization (it really depends on your use-case here, who should have access to this runner).
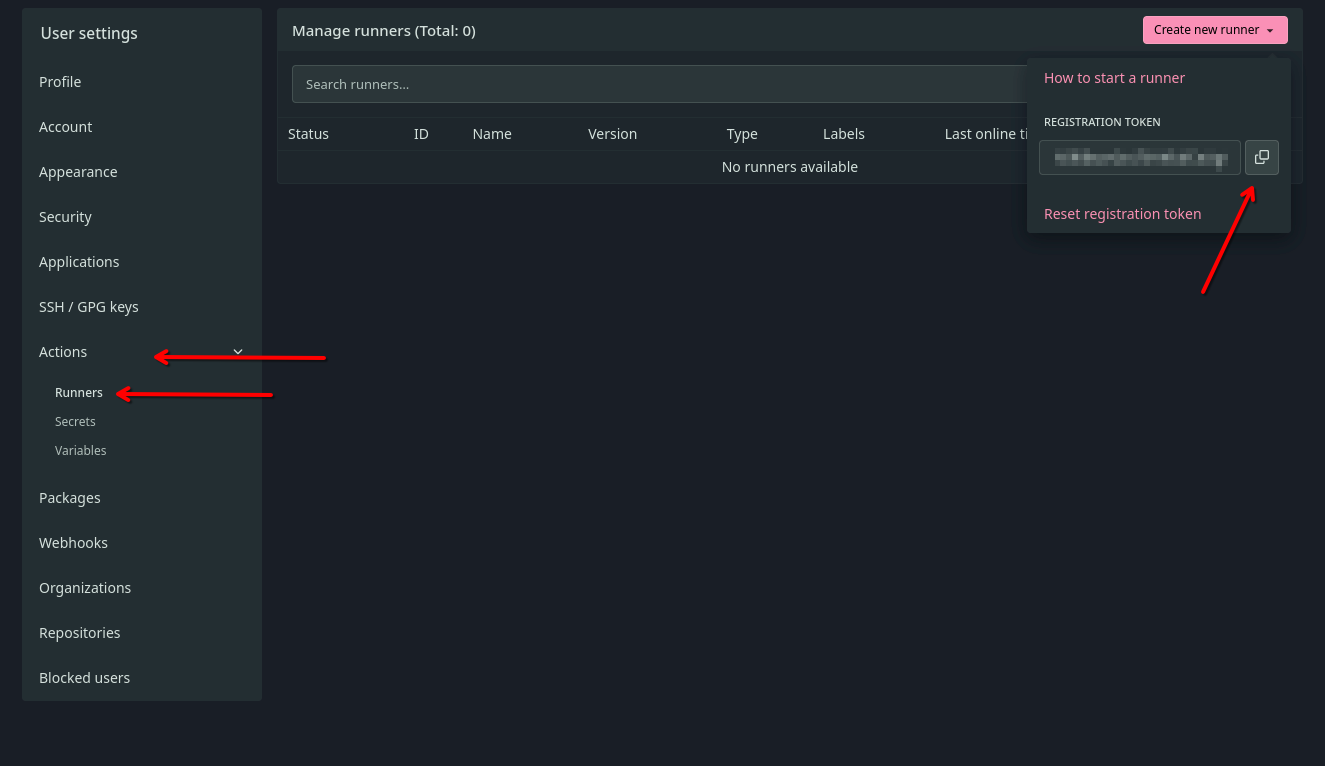
Once copied, proceed with registering the Forgejo instance on the runner. Note, we do not set --labels here, but you should pay attention to the official documentation if your setup requires a particular set of lables/
$ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'forgejo-runner register --instance https://yourdomain.tld/forgejo --name my-forgejo-runner --no-interactive --token lGr[REDACTED]pa5'
level=info msg="Registering runner, arch=amd64, os=linux, version=v11.2.0."
level=warning msg="Runner in user-mode."
level=debug msg="Successfully pinged the Forgejo instance server"
level=info msg="Runner registered successfully."Evidently, your token should not be lGr[REDACTED]pa5 but your actual token.
If you need additional configurations such as enabling IPv6, you can follow the official tutorial and setup a config file (don't forget to modify the followup daemon definition to point to the proper config with the --config flag). Otherwise, running this command should work without fault:
$ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'DOCKER_HOST=unix://$XDG_RUNTIME_DIR/podman/podman.sock forgejo-runner daemon'
time="2025-01-21T23:29:48Z" level=info msg="Starting runner daemon"
time="2025-01-21T23:29:48Z" level=info msg="runner: my-forgejo-runner, with version: v11.2.0, with labels: [docker], declared successfully"
time="2025-01-21T23:29:48Z" level=info msg="[poller 0] launched"
Once you verify that everything if properly setup, we can proceed to setup the systemd service/daemon. The following file is taken from the official guide (credits to Kwonunn and Kevin Ernst) and modified to properly use podman, as a user service. Put it as runner in /home/runner/.config/systemd/user/forgejo-runner.service . You can use ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost vim /home/runner/.config/systemd/user/forgejo-runner.service for example.
[Unit]
Description=Forgejo Runner
Documentation=https://forgejo.org/docs/latest/admin/actions/
After=podman.service
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/forgejo-runner daemon
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
Restart=on-failure
TimeoutSec=0
RestartSec=10
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
/home/runner/.config/systemd/user/forgejo-runner.service
Now you can enable (as runner) the service and run it.
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'systemctl --user daemon-reload'
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i .ssh/runner_key runner@localhost 'systemctl --user enable --now forgejo-runner'You should now see from forgejo that your runner is properly signed in.
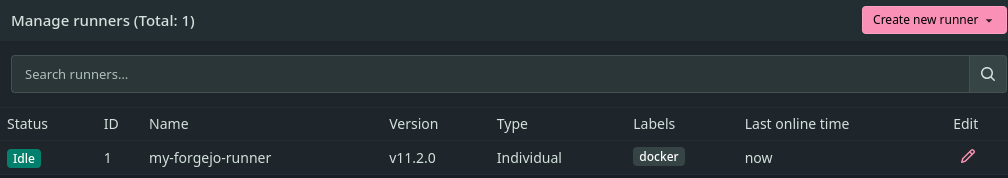
my-forgejo-runner properly registered on the forgejo instance.Et voilà. Enjoy.
Hachem